Pain, lumbago, constant weight, do you know such feelings in the back?
Harmless traction pain is often a sign of a dangerous disease. In this article, we will analyze all the causes of the disease.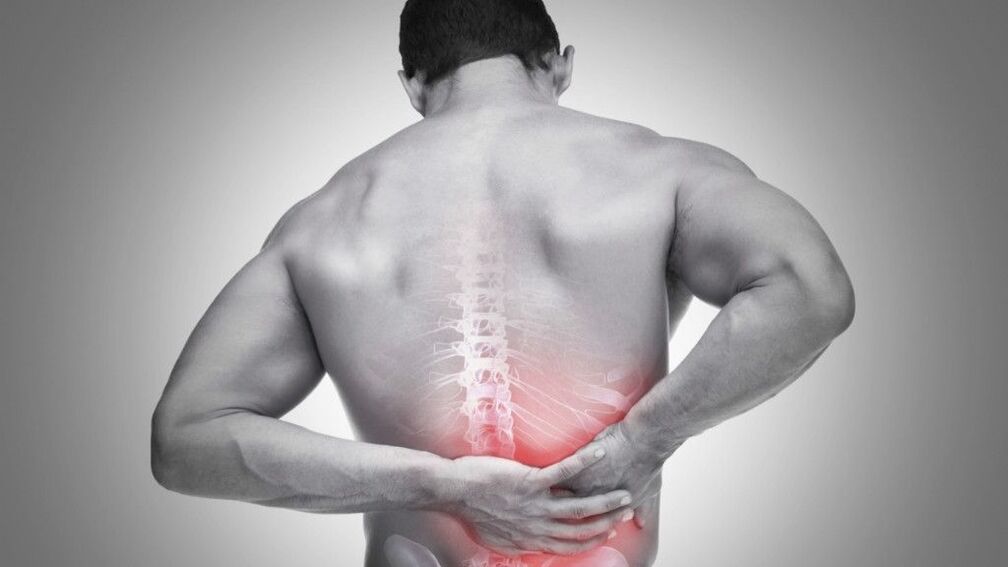
Causes
1. Diseases of the spine and pelvic bones.
- Osteochondrosis (damage to the intervertebral discs (bulge, disc herniation);
- Spondylitis (inflammatory disease of the spine);
- Spondyloarthritis (arthrosis of the intervertebral joints);
- Spondylosis (bone growth);
- Spondyloarthritis (inflammation of the intervertebral joints);
- Myositis (muscle inflammation);
- Osteoprosis (reduced bone density) with compression fractures of the vertebrae and other bone structures;
- Injury of the spine and pelvic bones (fractures, cracks);
- Sacroiliitis (inflammation of the sacroiliac joints);
- Tumors of bone structures and soft tissues.
2. Reflected pain in the lumbar spine,associated with diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs (inflammatory diseases and tumors), this pain is often accompanied by abdominal pain.
The nature of painmay be different:
- It is an acute pain that occurs quickly, suddenly;
- Chronic - pain longer than 2 months, occurs with progression of spinal disease;
- With inflammatory pathologies of the genitourinary system, abdominal organs (with chronic gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, enterocolitis).
Pain intensity
From discomfort to severe pain.
In the case of acute and intense abdominal pain radiating to the lumbar spine, it is always necessary to exclude surgical pathology that requires urgent surgical intervention (gastrointestinal bleeding, appendicitis, peritonitis, etc. ).
Intense pain in the lumbar spine
It can be reflex (muscle spasm caused by receptor irritation in the paravertebral muscles). It hurts a person when coughing, sneezing, all movements are accompanied by pain. When the nerve root is compressed (disc protrusion, disc herniation), the pain spreads to the lower extremities, often on one side.
Myofascial syndrome
It is caused by irritation of the receptors for pain in the muscles and fascia. There is the formation of triggers (pain nodules) in the muscles, the pain syndrome is chronic, often recurring.
Any trauma to soft tissues or bone structures is also accompanied by intense pain.
When to see a doctor: Any case of lumbar spine pain requires a visit to a doctor to diagnose the cause of the pain and take action.
Pain in men, women
With diseases of the reproductive system, the pain syndrome differs in men and women.
Men with prostate pathology are characterized by traction, aching pain, often accompanied by urinary incontinence. In women, the symptom is often acute, pronounced. With ovarian apoplexy or ectopic pregnancy, the pain is unbearable. Usually the syndrome is more intense on the affected side.
In endometriosis, uterine fibroids - painful sensations, withdrawal. If the pain is associated with spinal pathology, the intensity of the pain does not depend on gender. It has been observed that men later go to the doctor.
Diagnosis
Expert review
- vertebroneurologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- neurosurgeon;
- surgeon;
- gynecologist;
- urologist;
- rheumatologist;
- oncologist.
Laboratory methods
- general blood test (to rule out inflammation, leukocyte levels, ESR), exclusion of anemia (hemoglobin level);
- general analysis of urine: exclusion of the inflammatory process in the bladder, kidneys (bacteria, leukocytes, erythrocytes);
- fecal occult blood analysis;
- blood biochemistry: rheumatological tests to rule out systemic inflammation (CRP, RF, uric acid), assessment of liver function (alst ast bilirubin), assessment of renal function (creatinine urea), pancreatic function (amylase), etc.
Instrumental research methods
- radiography of the lumbar spine and pelvic bones; plain abdominal radiography (excluding intestinal obstruction);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- FGDS;
- colonoscopy;
- MRI (CT) of the lumbar spine, MRI (CT) of the lumbar spine with contrast;
- MRI (CT) of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis, MRI (CT) of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis with contrast.
Treatment
When a tumor is detected, depending on the location and nature of the tumor, tactics of treatment, surgery or others are determined (observation and treatment in neurosurgery, surgical hospital, oncology dispensary).
Drug treatment
Spinal diseases (more often in the context of osteochondrosis):
- NSAIDs;
- muscle relaxants;
- opioid analgesics;
- diuretic drugs;
- vascular drugs;
- antibacterial drugs;
- medical and medical blockade with novocaine, lidocaine, and diprospan.
Drug-free methods
They are mainly used in the treatment of spinal diseases:
- physiotherapy (magnetic laser, magnetotherapy, CMT with novocaine, etc. );
- acupuncture;
- lumbar spine hardware traction;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- balneotherapy (mud applications, ozokerite);
- Exercise therapy.

Prevention of spinal diseases (within osteochondrosis) by all the above methods (except physiotherapy).
Prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: diet, diet, work and rest.
If you have low back pain, go to the clinic.
The hospital has all the specialists and all the diagnostic methods presented in this article. There are also inpatient departments: the gastroenterology department and the city vertebrology center. All methods of treatment are used except surgery. You can be monitored, examined and treated on an outpatient basis, ie outside the hospital.













































